The United States Federal Reserve recently announced an unlimited Quantitative Easing (QE) program to provide cash to the economy in the wake of COVID-19 shutdowns, just weeks before Bitcoin goes through its next Quantitative Hardening (QH) event. What is Quantitative Hardening, and how does it differ from asset-buying programs known as Quantitative Easing? We did some research to help you understand these financial concepts.
Quantitative Hardening refers to a process by which a currency automatically becomes harder over time. A currency’s hardness refers to the difficulty in producing a new unit of that currency. Currencies that are easy to produce, like paper bills, often increase in quantity until they are worthless within a century. Currencies that are hard to produce, like pure gold coins, have held their value over millennia. The phrase Quantitative Hardening was coined by anonymous Twitter account @Schmiegle_ and popularized by Bitcoin figures such as Adam Back and Pierre Rochard.
What’s the difference between Quantitative Easing and Quantitative Hardening?
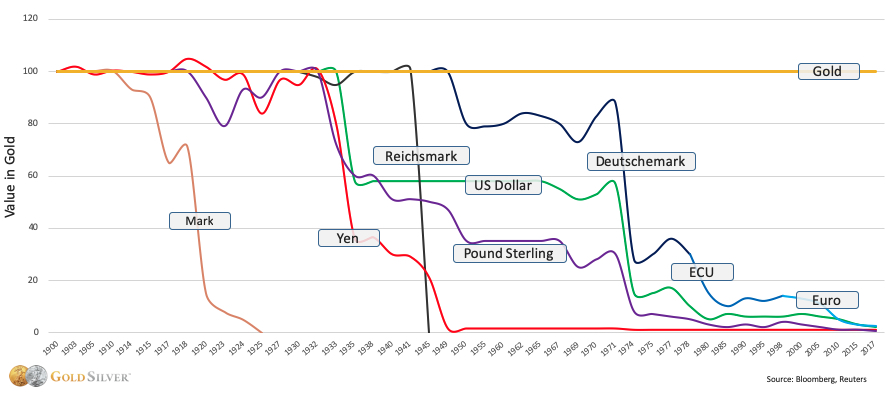
Quantitative Easing refers to central banks buying assets like government bonds, corporate bonds, and mortgage-backed securities in exchange for newly printed currency in order to provide the economy with more cash during a ‘liquidity crunch’. In a crunch, people are holding too many assets and not enough cash. When those assets fall sharply in value, as they did as a result of major selling following the COVID-19 panic, people suddenly find their assets are worth less than they thought, and they need cash. QE satisfies the immediate need for cash, but it comes with a price.
‘Easing’ refers to the fact that the central bank is making cash easier to acquire by pumping more of it into the system. However, when the crisis subsides, it can be difficult for the central bank to pull this cash back out of circulation. Those who received the new cash will begin to spend, causing prices to rise for the assets and goods they spend on. Following the 2008 bank bailout, financial assets saw huge rises in price – this was the banks spending their new cash.
In this way, fiat currencies usually become more easy over time, and rarely more hard.
Quantitative Hardening is a new concept originating in the algorithmic monetary policy of Bitcoin. The Bitcoin protocol is operated by a decentralized network of nodes, which makes it nigh impossible to make unilateral monetary policy decisions like bailouts funded by quantitative easing programs. Instead, the Bitcoin protocol emits a certain amount of Bitcoin in each “block” mined approximately every 10 minutes. On a regular schedule, roughly every 4 years, the number of new bitcoins emitted in each block cuts in half. This event is often referred to as a ‘Halving’ or ‘Halvening’.
As a result of these events, the bitcoin currency becomes harder over time.
How is the hardness of a currency measured?
The hardness of a currency can be measured in terms of its stock to flow ratio. The stock of a currency refers to the total outstanding amount in circulation, while the flow refers to the new amount of that currency produced over a given period of time – usually one year. The higher the ratio of stock to flow, the ‘harder’ the currency and the more immune it is to sudden increases in supply which hurt its value.
Gold’s Stock to Flow Ratio: 66
Gold has an annual stock to flow ratio of around 66, meaning it would take 66 years of gold mining at today’s rate of production to produce the entire existing stock of gold. This ratio has held consistently over time, as gold is very difficult and expensive to mine.
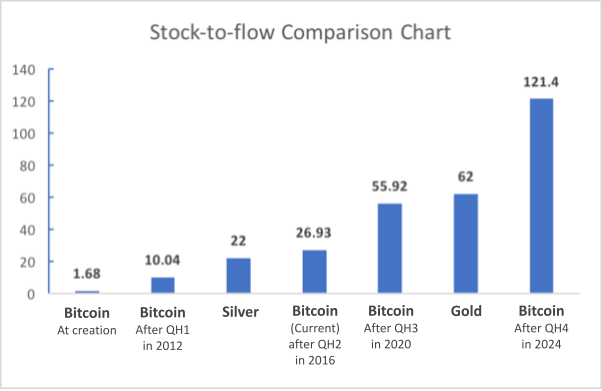
Bitcoin’s Stock to Flow Ratio: 55.92
Bitcoin’s stock to flow is simple to measure, because its monetary policy is clear and stable. Bitcoin’s annual stock to flow ratio is now 55.92. Bitcoin will surpass gold’s stock to flow in 2024, when QH4 will bring Bitcoin’s stock to flow ratio to around 112.
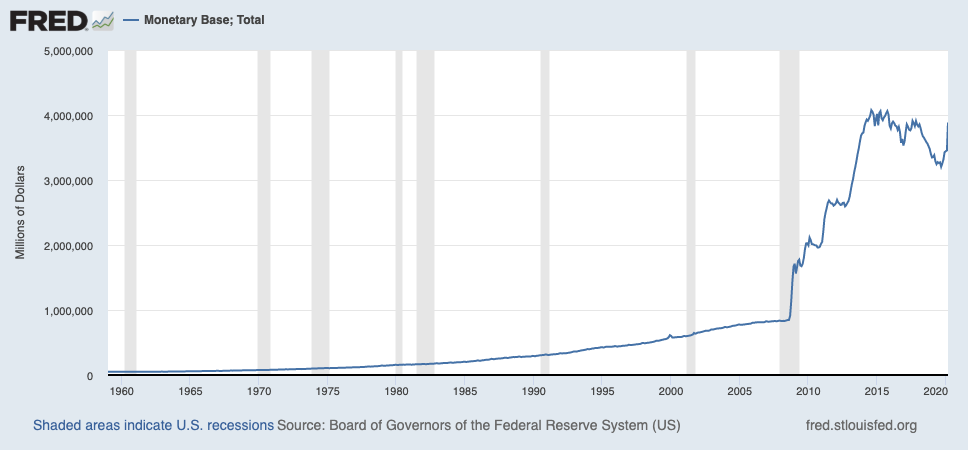
US Dollar Stock to Flow Ratio: 0.79
Fiat currencies like the US dollar do not have stable stock to flow ratios, since a small group of bankers and government officials determine when to produce more. For the US dollar, we can make an estimate using data on the growth of the monetary base: From 1960 to 2020 the stock to flow for dollars was 0.79, meaning that the number of dollars in circulation more than doubled every year, on average.

How do Quantitative Easing and Hardening affect me?
The COVID-19 crisis is leading the government to distribute a portion of currency from Quantitative Easing programs directly to citizens. Those who receive some of this new currency will want to spend or invest it quickly, as it will begin to devalue as soon as the economy picks up again.
You will feel the currency devaluing when you see rising prices from low post-crisis supply of goods and high demand coming from those who received new QE money. Those on a fixed income, like a salary or an hourly wage, feel the most pain since prices rise continuously, whereas salaries and wages usually increase only once a year.
Smart investors will use this new money to purchase hard assets, which serve as ‘hedges’ against the devaluing of currency – also known as inflation. When inflation causes fiat currencies to lose value, these hedges go up in value. Bitcoin is the biggest asset that features Quantitative Hardening events increasing its hardness over time.
Where can I buy hard assets?
Shares in holding companies that track the price of gold can be purchased on stock trading apps, but are susceptible to seizure by the government as President Roosevelt did in 1932 through Executive Order 6102.
Physical gold can be purchased at your local gold shop or from online gold stores like JMBullion, Schiff Gold, or GoldSilver.com, but often have a high starting price as the smallest unit is 1 ounce of gold, which costs almost $2,000 as of April 2020.
Bitcoin can be purchased online through apps like Cash App with as little as $5. To make easy recurring buys to “dollar cost average” (DCA) into Bitcoin, try River Financial or Swan Bitcoin.